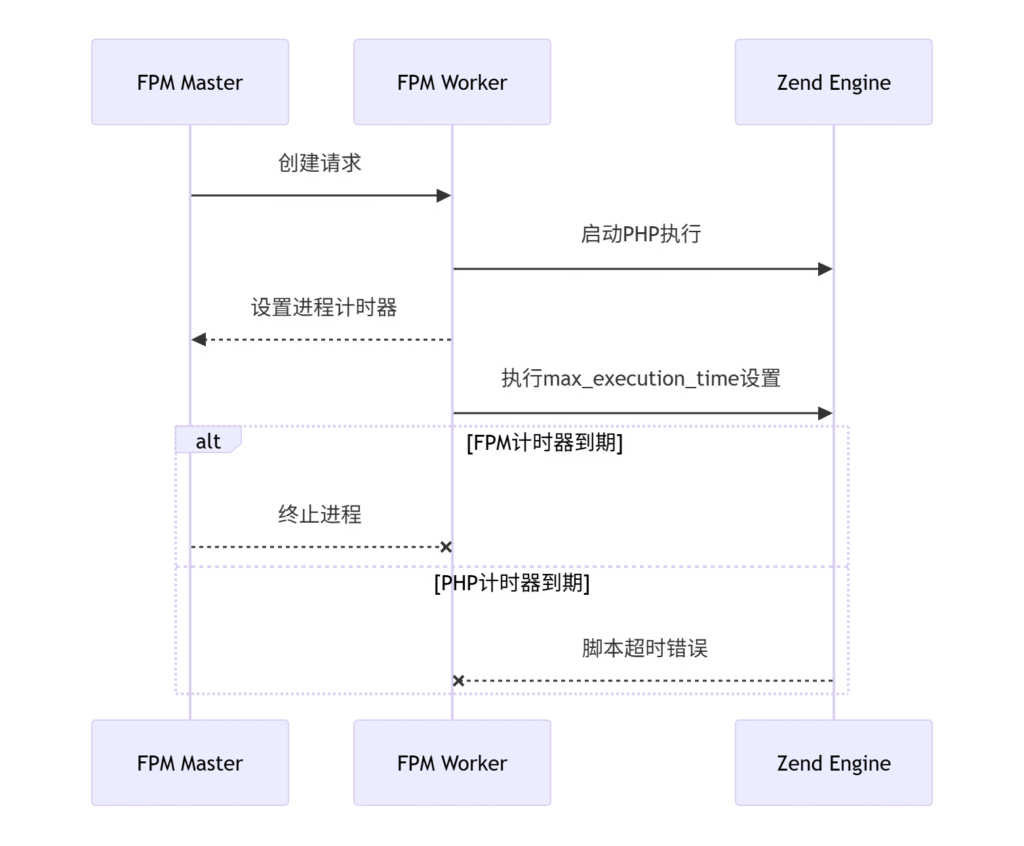
七牛cdn一定要开流量预警,没有预警的情况下是欠费后才能知道,好像有欠费不透支策略不过cdn流量统计有延时,盗刷流量如图所示:
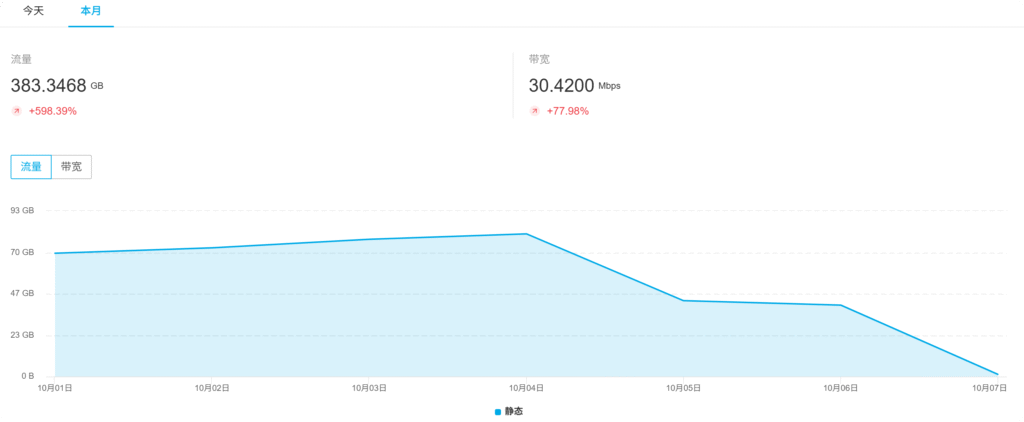
所有流量基本上都来自江苏,只刷特定一个图都高达几十GB,尽量不要把大图或者别的大的资源放到对象存储cdn加速。根据后台的统计分析,查看top100流量和次数的ip,如果是某些ip段的,直接整段封禁。查看刷的资源是什么,如果可以删除,就删除处理,然后在后台刷新预取文件刷新,刷新一下cdn缓存确保资源不能访问。一般刷cdn的也会刷网站首页,我安装了nginx openresty版本,可以使用lua脚本监控网站访问的ip,再根据ip段存入redis有序集合,同时存一份大于某个阈值ip的有序集合,可以监控异常ip访问。如下是监控到的ip段
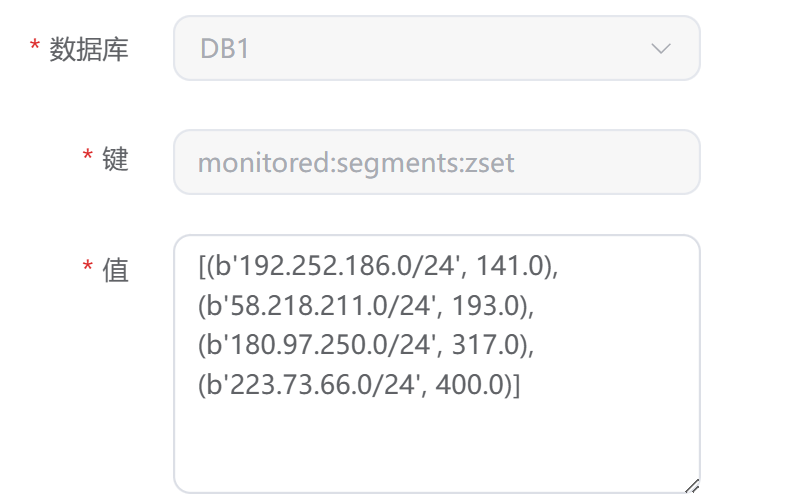
根据ip段去网站日志查询访问记录,果然发现了一个刷流量ip段
可以在nginx和七牛双向拉黑处理
nginx拉黑配置如下
geo $block_ip {
default 0;
# CIDR网段封禁
"58.222.32.0/24" 1;
"58.222.37.0/24" 1;
"58.222.48.0/24" 1;
"122.227.98.0/24" 1;
"180.97.235.0/24" 1;
"180.97.250.0/24" 1;
"180.118.170.0/24" 1;
"218.90.200.0/24" 1;
"218.90.204.0/24" 1;
"221.230.244.0/24" 1;
"222.186.16.0/24" 1;
"222.186.132.0/24" 1;
"222.186.159.0/24" 1;
"117.136.2.0/24" 1;
"117.136.47.0/24" 1;
}
server{
if ($block_ip) {
return 403;
}
location / {
access_by_lua_file /www/server/nginx/lua/auto_block.lua; # 指定Lua脚本路径
}
}
lua监控脚本如下
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeout(500)
-- 连接到Redis服务器并选择db1
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to connect to Redis: ", err)
return
end
local res, err = red:auth("xxx", "xxx")
if not res then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to authenticate Redis: ", err)
return
end
local ok, err = red:select(1) -- 使用db1
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to select database db1: ", err)
end
-- 获取客户端真实IP
local function get_client_ip()
local ip = ngx.var.remote_addr
local xff = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Forwarded-For"]
if xff then
ip = string.match(xff, '([^,]+)')
end
return ip
end
-- 正确提取/24网段的函数
local function get_ip_segment(ip)
local segments = {}
for segment in string.gmatch(ip, "%d+") do
table.insert(segments, segment)
end
if #segments == 4 then
return segments[1] .. "." .. segments[2] .. "." .. segments[3] .. ".0/24"
end
return "0.0.0.0/24" -- 默认值,防止错误
end
local client_ip = get_client_ip()
local segment = get_ip_segment(client_ip)
-- 定义统计Key和过期时间(1小时=3600秒)
local STAT_EXPIRE = 3600
local ip_count_key = "stat:ip:" .. client_ip
local segment_count_key = "stat:segment:" .. segment
-- 定义监控有序集合Key
local monitored_ips_zset = "monitored:ips:zset" -- IP监控有序集合
local monitored_segments_zset = "monitored:segments:zset" -- IP段监控有序集合
-- 使用管道提高性能
red:init_pipeline()
-- 统计IP访问次数(刷新过期时间)
red:incr(ip_count_key)
red:expire(ip_count_key, STAT_EXPIRE)
-- 统计IP段访问次数(刷新过期时间)
red:incr(segment_count_key)
red:expire(segment_count_key, STAT_EXPIRE)
-- 执行管道命令
local results, err = red:commit_pipeline()
if not results then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to commit pipeline: ", err)
else
local ip_count = results[1]
local segment_count = results[3]
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "IP ", client_ip, " count: ", ip_count,
" | Segment ", segment, " count: ", segment_count)
-- 检查是否需要加入监控有序集合(1小时内超过100次)
if ip_count > 100 then
-- 使用管道批量操作
red:init_pipeline()
-- 将IP加入有序集合,score=访问次数
red:zadd(monitored_ips_zset, ip_count, client_ip)
-- 刷新有序集合过期时间(24小时)
red:expire(monitored_ips_zset, 86400)
-- 刷新计数Key过期时间
red:expire(ip_count_key, STAT_EXPIRE)
local _, err = red:commit_pipeline()
if err then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to update IP zset: ", err)
else
ngx.log(ngx.WARN, "IP added to monitored zset (1h>100): ", client_ip,
" with score: ", ip_count)
end
end
if segment_count > 100 then
-- 使用管道批量操作
red:init_pipeline()
-- 将IP段加入有序集合,score=访问次数
red:zadd(monitored_segments_zset, segment_count, segment)
-- 刷新有序集合过期时间(24小时)
red:expire(monitored_segments_zset, 86400)
-- 刷新计数Key过期时间
red:expire(segment_count_key, STAT_EXPIRE)
local _, err = red:commit_pipeline()
if err then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to update segment zset: ", err)
else
ngx.log(ngx.WARN, "Segment added to monitored zset (1h>100): ", segment,
" with score: ", segment_count)
end
end
end
-- 保持原有连接池设置
red:set_keepalive(10000, 100)
还可以根据预警短信及时获取预警信息,根据自己的业务做拉黑处理,这里贴出七牛php sdk未收录的几个api,七牛官方通知支持短信和钉钉、飞书、企业微信的webhook。不过七牛的设置黑名单有一些问题,api提交以后,返回的是成功信息,这个成功信息是七牛放到队列成功不是配置成功,域名信息那里会显示配置中,但是千万不要以为会成功,有可能是失败的,所以即便cdn预警能hook到服务器,也可能黑名单不能及时配置成功,最终这个自动拉黑没有能实现,而且遇到问题工单也不能及时响应,所以不太建议使用七牛cdn。
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use Qiniu\Auth;
use Qiniu\Http\Error;
use Qiniu\Http\Client;
use Dotenv\Dotenv;
/**
* 获取某个cdn域名前100的访问
*/
class CdnManagerv2
{
private $auth;
private $server;
private $proxy;
public function __construct(Auth $auth)
{
$this->auth = $auth;
$this->server = 'https://fusion.qiniuapi.com';
}
/**
* https://developer.qiniu.com/fusion/4081/cdn-log-analysis#11
*/
public function getTopCountIp($domain)
{
$req = array();
$req['domains'] = [$domain];
$req['region'] = 'global';
$req['startDate'] = date("Y-m-d",time()-86400);
$req['endDate'] = date("Y-m-d");
$url = $this->server . '/v2/tune/loganalyze/topcountip';
$body = json_encode($req);
return $this->post($url, $body);
}
/**
* https://developer.qiniu.com/fusion/4081/cdn-log-analysis#12
*/
public function getTopTrafficIp($domain)
{
$req = array();
$req['domains'] = [$domain];
$req['region'] = 'global';
$req['startDate'] = date("Y-m-d",time()-86400);
$req['endDate'] = date("Y-m-d");
$url = $this->server . '/v2/tune/loganalyze/toptrafficip';
$body = json_encode($req);
return $this->post($url, $body);
}
private function post($url, $body)
{
$headers = $this->auth->authorization($url, $body, 'application/json');
$headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json';
$ret = Client::post($url, $body, $headers, null);
if (!$ret->ok()) {
return array(null, new Error($url, $ret));
}
$r = ($ret->body === null) ? array() : $ret->json();
return array($r, null);
}
}
/**
* 获取域名信息和设置黑名单
*/
class DomainManager
{
private $auth;
private $server;
public function __construct(Auth $auth)
{
$this->auth = $auth;
$this->server = 'https://api.qiniu.com';
}
/**
* https://developer.qiniu.com/fusion/4246/the-domain-name#10
*/
public function getDomainInfo($domain)
{
$url = $this->server . "/domain/".$domain;
return $this->get($url,'');
}
/**
* https://developer.qiniu.com/fusion/4246/the-domain-name#16
*/
public function putIpacl($domain,$ips)
{
$url = $this->server . "/domain/".$domain."/ipacl";
$body = ['IPACL'=>['ipACLType'=>"black","ipACLValues"=>$ips]];
$body = json_encode($body);
$headers = $this->auth->authorization($url,$body, 'application/json');
$headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json';
$ret = Client::PUT($url,$body,$headers);
if (!$ret->ok()) {
return array(null, new Error($url, $ret));
}
$r = ($ret->body === null) ? array() : $ret->json();
return array($r, null);
}
private function get($url,$body)
{
$headers = $this->auth->authorization($url,$body, 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
$headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';
$ret = Client::get($url, $headers);
if (!$ret->ok()) {
return array(null, new Error($url, $ret));
}
$r = ($ret->body === null) ? array() : $ret->json();
return array($r, null);
}
}
$dotenv = Dotenv::createImmutable(__DIR__);
$dotenv->load();
$accessKey = getenv('QINIU_ACCESS_KEY');
$secretKey = getenv('QINIU_SECRET_KEY');
$cdn_domain = getenv('CDN_DOMAIN');
$auth = new Auth($accessKey, $secretKey);
$domainManager = new DomainManager($auth);
$info = $domainManager->getDomainInfo($cdn_domain);
$ipACLValues = $info[0]['ipACL']['ipACLValues'];
$ipACLValues = require_once "blackips.php";
$put_ret = $domainManager->putIpacl($cdn_domain,$ipACLValues);
$cdn_manager_v2 = new CdnManagerv2($auth);
$cdn_count = $cdn_manager_v2->getTopCountIp($cdn_domain);
$cdn_data = $cdn_count[0]['data'];
$cdn_data_com = array_combine($cdn_data['ips'],$cdn_data['count']);
$cdn_trafic = $cdn_manager_v2->getTopTrafficIp($cdn_domain);
$cdn_trafic_data = $cdn_trafic[0]['data'];
$cdn_trafic_com = array_combine($cdn_trafic_data['ips'],$cdn_trafic_data['traffic']);
$ip2region = new \Ip2Region('file',__DIR__.'/vendor/zoujingli/ip2region/db/ip2region_v4.xdb');
foreach($cdn_data_com as $key => $value){
echo mb_convert_encoding($ip2region->simple($key),'GBK', 'UTF-8').$key."<br/>"; // 中国广东省中山市【电信】
}